Why Single Page SEO Matters
Single-page websites are becoming popular among SaaS brands and portfolios because they offer a fast and simple user experience. Instead of clicking through multiple pages, users only need to scroll to view all the content on a single page.
However, single-page SEO is more complex in nature. Given the fact that Google favors websites publishing information related to multiple URLs, single-page SEO is more complicated in terms of keyword targeting. Despite this complexity, single-page SEO is most effective in terms of engagement and loading speed.
With this guide, you will be able to follow a clear, step-by-step plan for optimizing your single-page site for the year 2026. It will show you how your site can rank higher in search engine results by creating or avoiding certain things.
What Is a Single-Page Website?
A single-page website is a site that contains all its content on one long scrolling page instead of separate URLs for different topics. Navigation usually works through anchor links that jump to sections like Features, Pricing, About, or Contact.
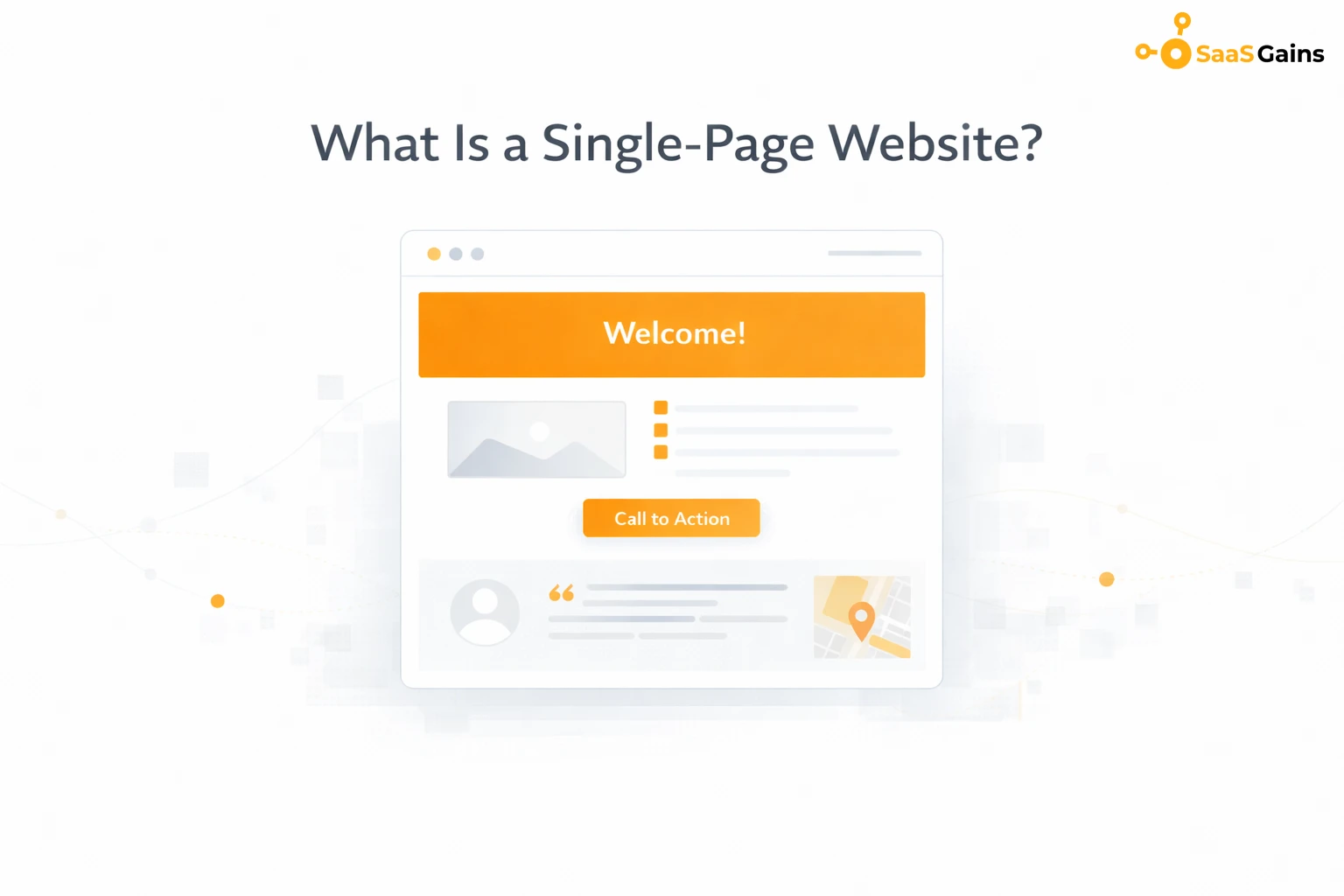
This structure works best for simple websites that do not need complex content. Common use cases include:
- SaaS landing pages: High-conversion pages designed to explain a software solution.
- Website for events: Single location for dates, speakers, and registration.
- Personal portfolios: An efficient and professional way to present work.
- Product launch page (PLP): A targeted page designed for launching a new product and generating buzz around its release.
- Start-up homepages: Straightforward launch announcements of a new model of doing business.
For example, a SaaS product landing page can explain features, pricing, and contact details on a single page. Users scroll instead of clicking through different pages, which creates a smooth experience.
Pros and Cons of Single-Page SEO
Pros
Focused Messaging
Single-page websites keep messaging focused. There is one main theme instead of scattered topics across multiple URLs.
Concentrated Authority
They also concentrate link equity on a single page, which can make it easier to build authority if done correctly.
As Jamie Grant explains:
“All backlinks that are built to your site will point toward a single URL.”
This means all PageRank flows directly to one page without dilution from internal linking.
Enhanced Performance
Because there are fewer files to load, single-page sites are often faster and deliver a better user experience.
Simplified Maintenance
Managing content is also easier since everything lives in one place.
Cons
Keyword Limitations
The biggest SEO limitation is keyword targeting. You cannot rank for many different topics because everything is on one URL.
Topical Authority Gaps
It is also harder to build topical authority when you do not have separate cluster pages.
Analytics Complexity
Tracking user behavior is more difficult since analytics segmentation across multiple pages is limited.
Clear Goal: Start With the Right SEO Strategy
Before optimizing anything, you need one clear main keyword or theme. A single-page website cannot target everything, so focus matters. Your page goal should match your business objective.
For example, if your goal is leads, your content should support conversions rather than broad education. If your site is a product landing page, you should follow proven landing page SEO strategies that focus on both rankings and conversions.
Keyword Research and Section Mapping
Your main keyword should define the purpose of your page. This might be something like single-page website SEO or one-page website optimization. Then choose three to five supporting long-tail keywords that naturally fit into different sections of your page.
Each supporting keyword should match a specific section. For example:
- H2 Page Speed Optimization: Could target the keyword “single-page website speed.”
- H2 Mobile SEO: Could target the keyword “mobile-friendly one-page SEO.”

Structuring Content So Google Understands Sections
Your H1 should clearly reflect the main intent of your page. Each H2 and H3 should answer specific user questions related to your topic. Anchor-based navigation improves both user experience and SEO by making sections easy to find.
Clear structure also helps Google understand that your single page still covers different subtopics in an organized way.

Google’s Senior Search Analyst John Mueller confirms this flexibility with headings:
“Our systems don’t have a problem when it comes to multiple h1 headings on a page. That’s a fairly common pattern on the web. We use headings to better understand the context of different parts of a page. Our systems aren’t too picky and we’ll try to work with the HTML as we find it, be it one H1 heading, multiple H1 headings or just styled pieces of text without semantic HTML at all.”
Meta Title and Description That Convert
Your meta title should contain your target search term and should be action-oriented.
- Example Title: Single Page Website SEO (2026): Rank Faster & Get Traffic
The purpose of your meta description is to describe the benefit of your guide.
- Example Description: Learn how to optimize single-page website SEO with effective strategies to improve visibility, user experience, and rankings in search engines
This lets users and Google know what your page provides
Page Speed and Performance Optimization
Speed is one of the most important factors to consider when optimizing for ranking, especially for single-page sites. Loading slow pages are frustrating to users and penalized by search engines. To achieve optimal performance, you are recommended to:
- Compress Images: Images should be compressed to make the image size smaller without reducing the image quality.
- Minify JavaScript/CSS: Remove redundant characters from code to reduce the burden on the browser.
- Lazy-loading images and videos: Load images and videos when the user scrolls down to them to save the initial bandwidth.
- Use a content delivery network: Serve your content from servers spread across the globe to minimize the distance that data must travel to the user.
On-Page SEO Best Practices

- Heading Hierarchy: Use unique headings that include relevant keywords to guide the reader.
- Visual Optimization: Add descriptive alt text to images instead of generic labels to help search engines “see” your media.
- Keyword Context: Use semantic keywords that naturally support your main topic to build topical depth.
- Navigational Clarity: Optimize internal anchor text so users clearly understand where links lead.
For deeper internal linking strategies, check our article on internal linking best practices.
Schema and Structured Data
Adding schema helps search engines better understand your content. You can use:
- Organization schema: Identifies your brand and social profiles.
- FAQ schema: Displays common questions and answers directly in search results.
- Product or service schema: Highlights specific offerings, prices, or reviews.
This can also improve your chances of rich results in search.
Improve Readability and Engagement
- Content Spacing: Break content into short paragraphs to avoid overwhelming the reader.
- Lists: Use bullet points where helpful to make technical information easy to digest.
- Formatting: Highlight key ideas in bold to guide the user’s eye to the most important points.
- Conversions: Add clear calls to action if your goal is leads or sales.
Good readability keeps users on your page longer, which sends positive signals to Google.
Visuals That Support Content
Use diagrams, screenshots, and mockups to explain complex ideas. Always include keyword-rich alt text that describes what the image shows. Visuals make your single page more engaging and easier to understand.
Backlink and Outreach Strategy
Because you only have one URL, all backlinks should point to that page. You can build links through:
- Guest posts: Write for other industry blogs and link back to your one-page site.
- Resource pages: Get your site listed as a helpful resource in your specific niche.
- Social promotion: Use social sharing to drive traffic and attract natural citations.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with industry peers for mentions and co-marketing efforts.
If you run a SaaS company, our guide on SaaS backlink strategy can help you scale your efforts.
Track Performance and Refine
Use Google Analytics to monitor:
- Bounce rate: See if users are leaving without interacting.
- Scroll depth: Track how far down the page users are actually traveling.
- Time on page: Measure how long users stay engaged with your content.
Use Google Search Console to track:
- Impressions: How many times your site appears in search results.
- Click-through rate (CTR): The percentage of users who click your result.
- Average ranking position: Your overall standing for your target keywords.
Regular analysis helps you refine your strategy over time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-optimization: Do not stuff keywords unnaturally.
- Vague Navigation: Avoid unclear anchor labels like “click here.”
- Mobile Neglect: Do not ignore mobile user experience; ensure the page is responsive.
- Blind Strategy: Always track your metrics instead of guessing performance.
Conclusion
Single-page SEO is challenging, but it is absolutely possible in 2026 if done correctly. With the right structure, fast performance, and consistent monitoring, you can rank and drive traffic even with one page. This format works especially well for SaaS landing pages, event websites, and portfolios. If you plan carefully and optimize continuously, a single-page website can still perform strongly in search.