Duplicate content used to be a minor technical glitch. In 2026 it has become a major roadblock for growth. If your website has the same text as other sites, you are telling Google you have nothing new to offer. Search engines now prioritize original ideas over repeated facts.
This guide will help you fix these issues. We will explore why duplication happens and how to protect your rankings. You will learn to make your site a trusted source of truth for both AI agents and human readers.
What is Duplicate Content Today?
Duplicate content happens when large blocks of text appear in more than one place. This can be on your own site or across the web. In 2026 Google uses very high standards for what counts as unique. It is no longer just about matching words. It is about matching the intent and value of the information provided.
Internal Duplication
This occurs inside your own website. It usually happens because of your site settings.
- Session IDs These track visitors but create many identical links for the same page.
- Search Parameters Filters for size or color can create duplicate versions of one page that search bots get stuck on.
- Service Pages Using the same description for different locations makes your site look like a template rather than a real business.
External Duplication
This is when your text appears on other websites.
- Scraper Sites Bots that steal your blog posts to build their own traffic often outrank you if you do not have strong authority.
- Content Syndication Posting your articles on sites like Medium or LinkedIn without the right tags.
- Product Descriptions Using the exact text provided by a manufacturer that every other store uses makes it impossible to rank on page one.
Why It Matters for 2026 Ranking?
Search engines focus on efficiency and energy savings. They do not want to crawl the same information twice. Here is how duplication hurts your business.
Information Gain Score
Google now rewards sites that add new facts. If you just repeat what others say, your ranking will drop. Google defines this through a specific metric called an information gain score.
Experts agree that providing new information that the searcher has not seen yet is the only way to stay relevant in an AI-heavy search world.
Crawl Budget Waste
Google only spends a certain amount of time on your site. This is called a crawl budget. If it finds 50 versions of one page, it might stop looking before it finds your best content. This is a major issue for large sites that need frequent updates to stay fresh.
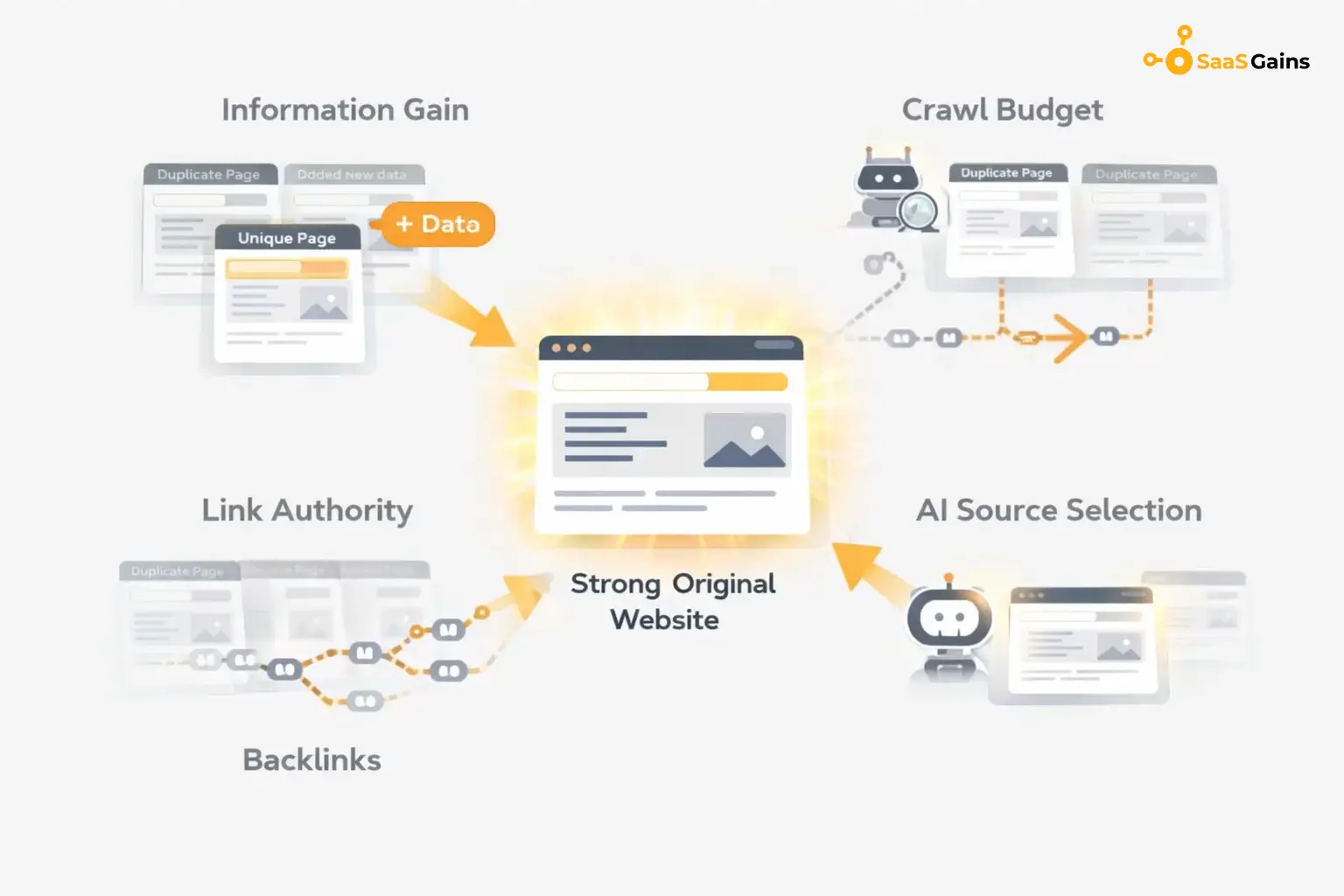
Diluted Link Power
Backlinks are like votes. If you have two versions of a page, those votes are split between them. This makes it much harder to reach the first page of results because neither page has enough power. You are essentially competing against yourself and losing.
AI Source Selection
AI agents like Gemini or SearchGPT want one clear answer. If they find many versions of your data, they may ignore you entirely. They will choose a site that looks more stable and original to cite as their primary source. If you are not the original source, you do not get the traffic.
The 2026 GEO and Information Gain Gap
To beat your competitors, you must address the gaps they often miss. Most basic guides ignore how AI handles near duplicates or thin content.
The Information Gain Score Explained
Information gain refers to a score that indicates the additional information included in a document beyond what is already on the web. In 2026 this is a core ranking factor. If your article does not offer a new perspective or a unique data set, it will be hidden behind the original source. You must ask yourself what you are saying that no one else is.
Writing for AI Citation (GEO)
Generative Experience Optimization, or GEO, is the practice of making your content easy for AI models to extract and cite.
- Use direct answer blocks at the start of sections to help AI find the main point.
- Keep your sentences simple and factual so the machine can verify them easily.
- AI systems prefer content that is contextual and semantically clear over content filled with keywords.
Semantic and Intent Duplication
A semantic gap happens when you have two pages that use different words but answer the exact same question. In 2026 Google sees these as duplicates because the user intent is identical. For example, having one page for SEO Tips and another for SEO Advice is redundant. You must merge these pages into one comprehensive Power Page.
How to Find Duplicate Content Issues?
You cannot fix what you cannot see. Experts use specific tools to find these hidden traps before they cause a drop in traffic.
| Tool Name | What It Finds | Expert Tip |
| Screaming Frog | Identical Titles | Check your H1 tags for any repeats across your site |
| Copyscape | Plagiarism | Use this regularly to see if competitors are stealing your text |
| Search Console | Indexing Errors | Look at the Pages report for Duplicate Google chose different canonical than the user |
| Originality AI | Lack of Insight | Ensure your content does not sound like generic AI-generated text |
Smart Fixes for Your Website
Fixing these issues is about giving Google a clear path. You must tell the search engine which page is the master version.
Use the Canonical Tag
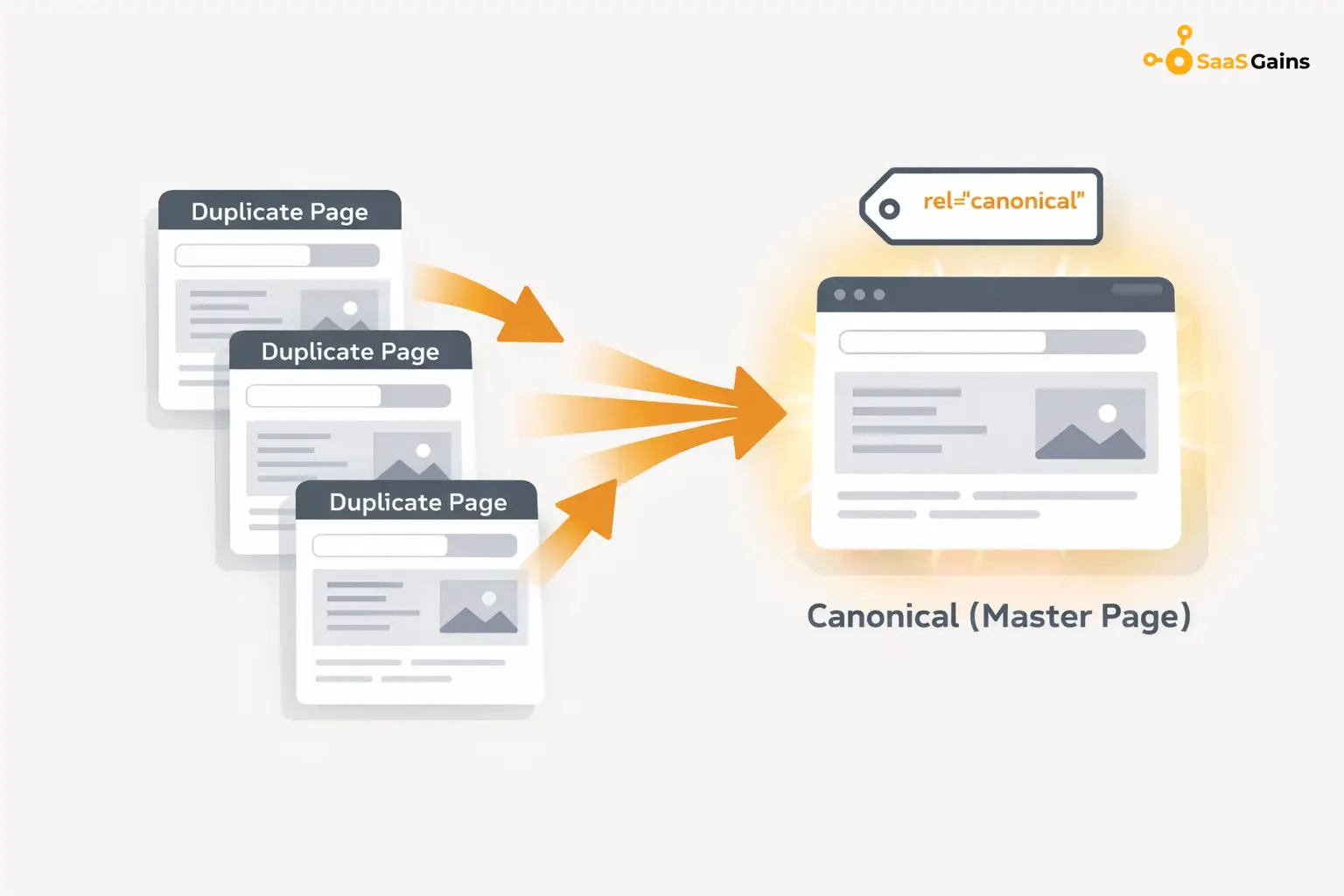
This is a small piece of code. It tells Google that a page is a copy. It points the search engine to the original version.
A canonical URL is the URL of the page that Google thinks is most representative from a set of duplicate pages on your site. Using this tag helps concentrate all your ranking signals onto one powerful page. This is the gold standard for fixing technical duplication.
Set up 301 Redirects
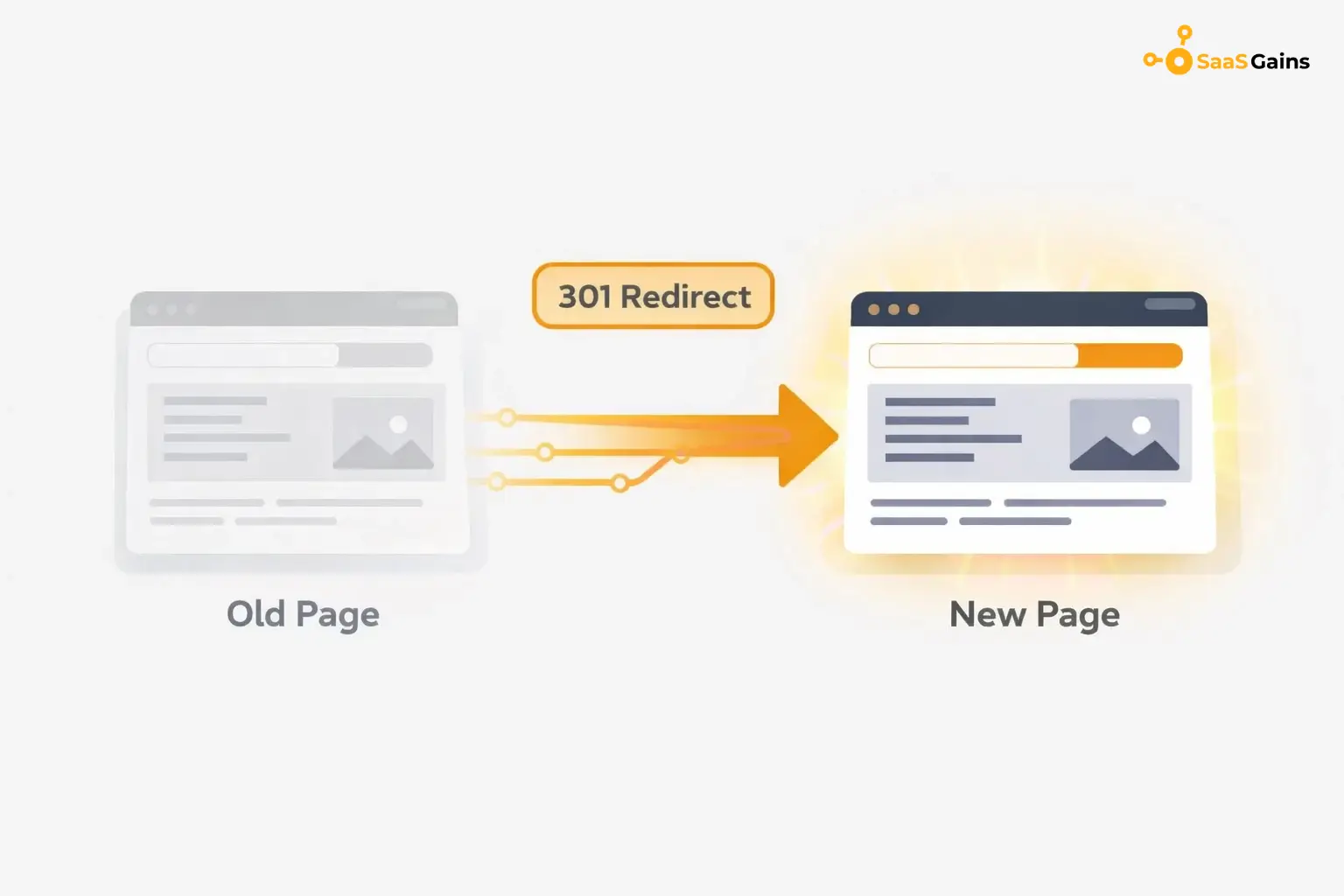
If you have two identical pages, you should combine them. A 301 redirect sends users from the old page to the new one. This is the most effective way to clean up your site and keep your link power. It tells the browser and the search engine that the page has moved permanently.
Add Unique Perspectives (GEO Optimization)
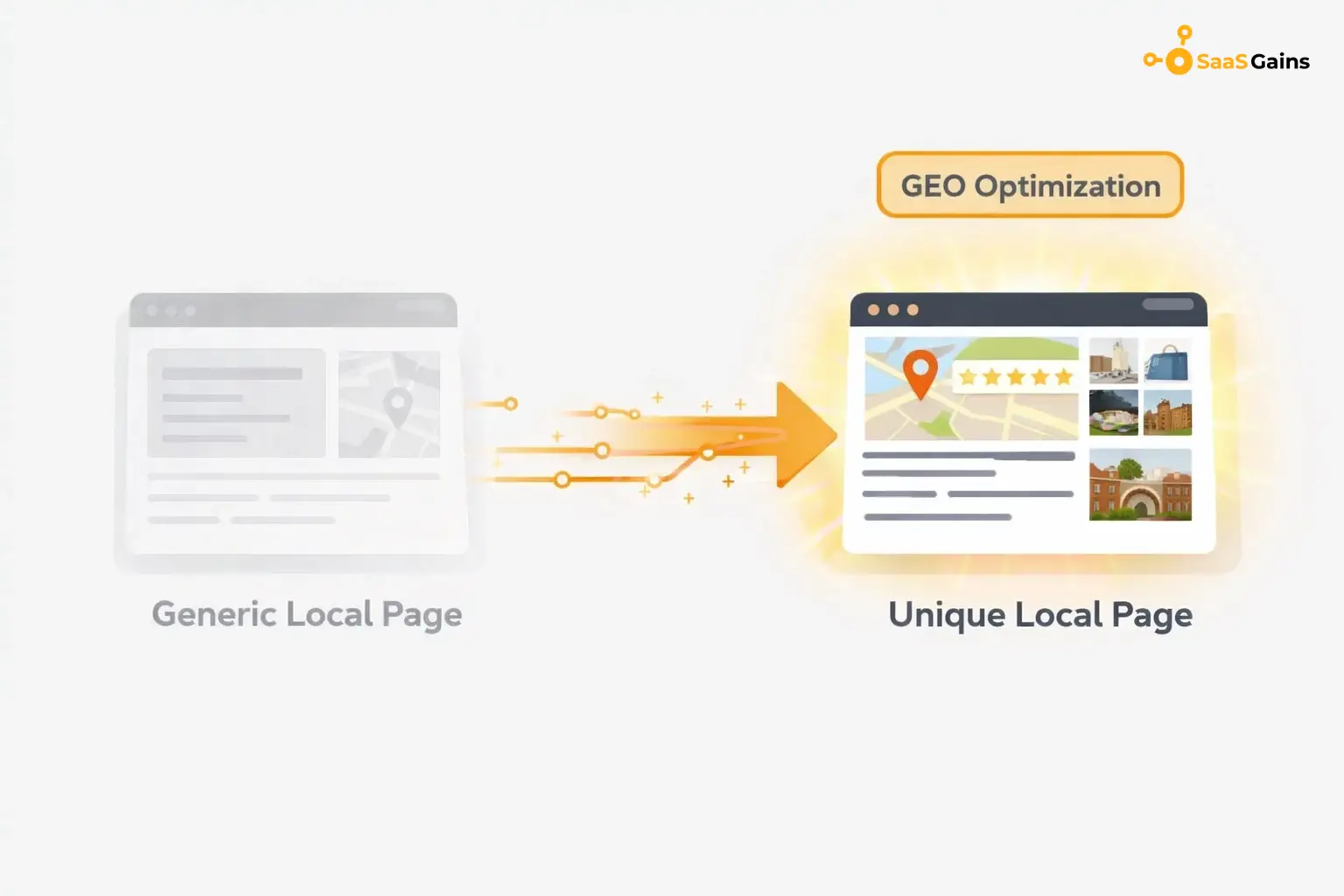
For local pages you should not just change the city name. This is now flagged as scaled content abuse.
- Add local reviews from customers in that specific city.
- Post photos of your team working in that area to show real presence.
- Mention local landmarks or specific local problems you solve to prove you are relevant.
Google states that scaled content abuse is when pages are generated at scale for the primary purpose of manipulating search rankings and do not provide original content.
Technical Infrastructure for AI Agents
In 2026 you are not just ranking for humans. You are ranking for AI agents that browse the web for users. Your technical setup must be perfect.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) Ensure your page is fast. AI agents move to the next source if a page takes more than 200 milliseconds to respond. Speed is now a core part of being a trusted source.
- Server-Side Rendering Provide your key answers in the initial HTML. Some AI crawlers are fast and do not wait for heavy JavaScript to load. If the answer isn’t in the HTML, they won’t cite you.
- Nested Schema: Use structured data to connect your authors and your organization to the content. This builds the trust signals that AI models crave. It tells the machine exactly who is responsible for the information.
Best Practices for Content Syndication
Republishing your content can help you reach a wider audience, but it must be done carefully to avoid harming your site’s rankings.
Wait at least one week before republishing your blog on other platforms. This gives Google enough time to crawl and index your website as the original source.
Always include a clear attribution link such as:
“This article originally appeared on [https://saasgains.com/blog/why-is-having-duplicate-content-an-issue-for-seo/].”
Proper attribution helps search engines and AI systems correctly identify the original source of the content. Backlinko also recommends using self-referencing canonical tags on original posts to ensure scrapers or syndicated versions are not treated as the primary source.
Conclusion
Duplicate content is a major hurdle in the modern search era. It confuses search engines and wastes your site resources. By using tags like canonicals and redirects, you can protect your SEO health.
The goal for 2026 is clear. You must provide unique value on every page. This ensures you remain a top choice for both human readers and AI search agents. Focus on originality, and your rankings will follow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Google penalize me for duplicate content?
Google does not usually give a manual penalty for this. Instead, it just hides the duplicate pages from results. This makes your site lose traffic even if you are not officially banned. It is a penalty of invisibility.
How much of a page needs to be unique?
Most experts suggest at least seventy percent of your content should be unique. This includes your specific tone and unique data points that no one else has.
Can AI content cause duplicate issues?
Yes, it can. If you use AI to write generic text, it will look like thousands of other sites. You must edit AI text to include your own brand stories and real-life examples to avoid being filtered out.
What is a self-referencing canonical?
This is a tag on your main page that points to itself. It tells Google that this page is definitely the original. It is a best practice for every page on your site to prevent external duplication issues.
How do I fix duplicates on local landing pages?
Do not use the same template for every city. Add local reviews and photos of your team in that city. This makes the page unique for both users and search engines.




