Earning a top spot in search engine results is a goal for every website owner. However, the methods used to get there determine whether a brand thrives or disappears. While high-quality links are the backbone of authority, many people unknowingly risk their entire digital future by using link farms.
Understanding the meaning of link farming is the first step toward protecting your website. This guide offers a professional look at how to identify these risks and build a strategy based on real trust. By choosing quality over speed, you ensure that your website remains safe and visible for the long term.
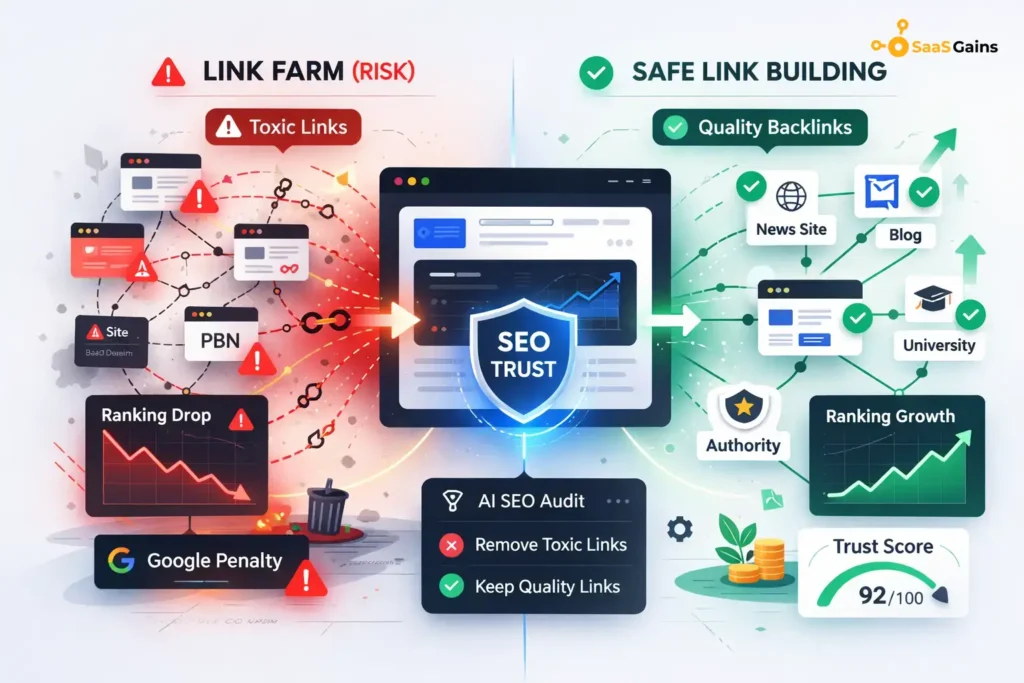
What is a link farm?
To understand the risks, you must first know what is a link farm. A link farm is a group of websites built only to link to other pages. These sites offer no value to readers and usually feature low-quality, unrelated content.
When you see a site from a link farm, you will notice it lacks a clear brand or audience. It exists only to fake popularity for sites that pay for links. Because these platforms link to anyone, they lack the authority and trust that search engines require.
Why People Use Link Farming?
- They believe a high number of links is more important than quality
- They are looking for a cheap way to increase their search rankings
- They want to see results in a few days rather than waiting months
- They do not realize that modern algorithms can easily spot fake link patterns
The Serious Risks of What is Link Farming
Many beginners ask what is link farming in terms of its effect on a business. It is a black hat tactic that violates the rules of search engines. Major platforms want to provide the best experience for their users, and they actively penalize sites that try to cheat the system.
If your site is caught using link farms, you may face a manual penalty. This means your website could be pushed down hundreds of pages in search results or removed entirely.
According to industry experts, over 96.55% of pages with no organic traffic are often those that lack high-quality authoritative backlinks or have been penalized for manipulative tactics.
How to Identify Link Farms Effectively?
Knowing how to spot these sites is essential for every SEO-focused person. Most link farms have specific warning signs that are easy to see if you know where to look. Here is how to evaluate a site before you decide to work with it.
Analyze the Content Quality
A real website has a clear voice and helpful information. A link farm often uses AI-generated or spun content that makes very little sense. If the articles are full of grammar errors and offer no real insight, it is a major red flag.
Check for Niche Relevancy
Natural websites stay within a specific industry. If you see a blog that posts about “best power tools” one day and “how to trade crypto” the next, it is likely a site built for link farming. Search engines prefer links from sites that are relevant to your own business.
Look at Traffic Trends
Use a tool like Ahrefs to check the organic traffic of a site. A healthy website should have a steady flow of visitors. If a site has a high domain rating but zero organic traffic, it is almost certainly a link farm.
Strategic Alternatives to Link Farming
The best way to avoid link farms is to use tactics that build genuine authority. These methods may take longer, but they provide a foundation that search engines respect.
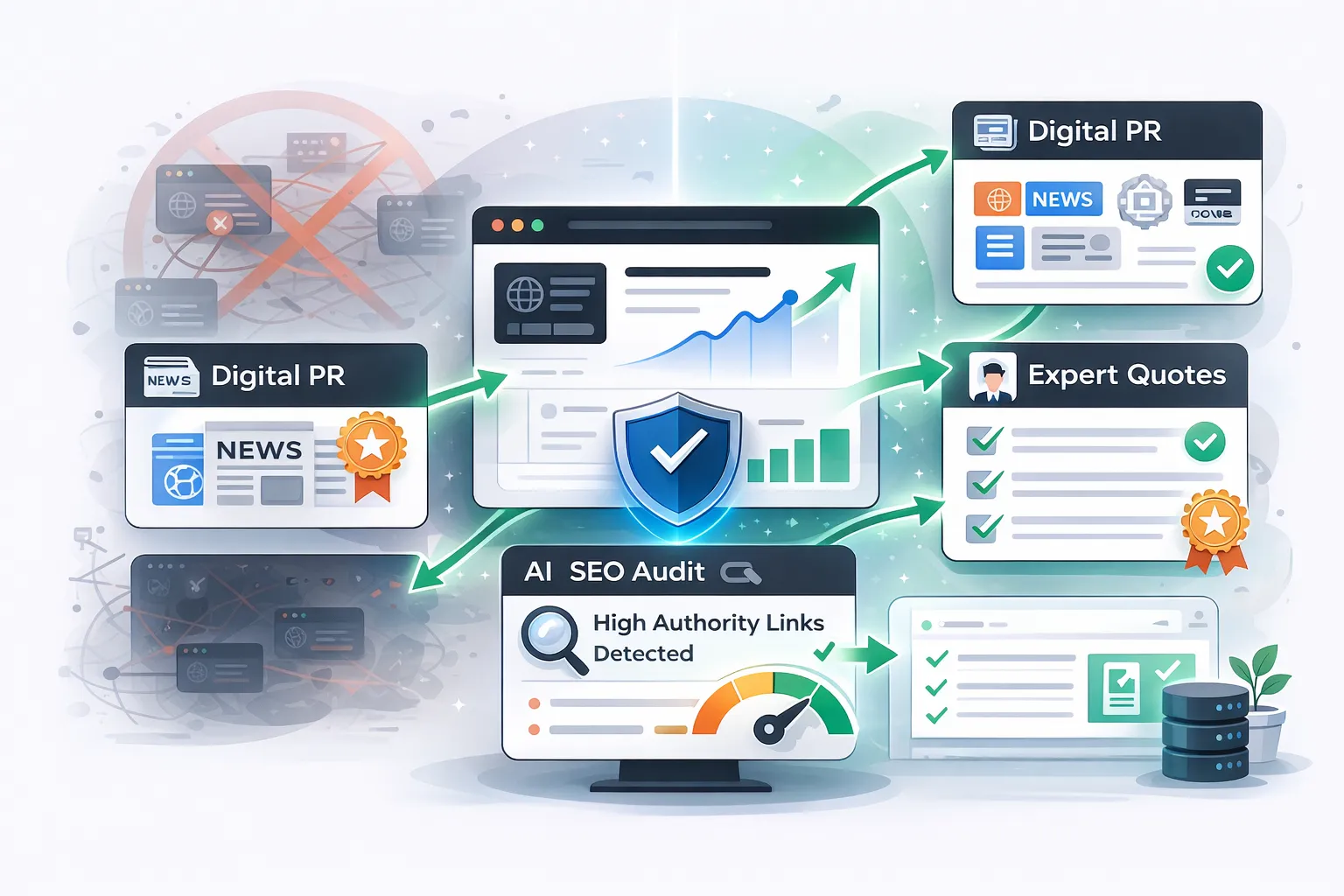
The Power of Digital PR
Digital PR involves getting your brand mentioned in reputable news outlets and industry publications. This is the opposite of link farming because it relies on being newsworthy. One link from a major news site is worth more than thousands of links from low-quality farms.
Resource Page Link Building
Find websites that have a “Resources” or “Tools” page for your industry. If you have a helpful guide or a free tool, you can reach out to the site owner and ask to be added. This results in a high-quality link that actually drives traffic to your site.
Expert Quote Contributions
Many writers look for expert opinions to add to their articles. By providing a unique insight or a helpful quote, you can earn a backlink from a high-authority site. This builds your reputation as an expert and avoids the risks associated with link farm tactics.
Why Search Engines Target Link Farms?
The primary goal of a search engine is to keep its results clean and helpful. If link farming were allowed, search results would be full of poor-quality sites. To prevent this, algorithms use complex patterns to identify unnatural link growth.
They look at the “link neighborhood” of your site. If your website is surrounded by known link farms, it tells the search engine that you are trying to manipulate the results. This results in a loss of trust that can be very difficult to regain.
Link Quality vs Quantity Comparison
| Feature | High-Quality Link | Link Farm Link |
| Trust Level | Very High | Very Low |
| Risk of Penalty | None | High |
| Traffic Source | Real Users | Automated Bots |
| Long-Term Value | Increases over time | Decreases or disappears |
| Cost | Earned through value | Often paid for directly |
How Can Link Farming Be Avoided Completely?
To protect your business, you must be disciplined in your outreach strategy. Here are the best practices for avoiding accidental involvement with link farms.
- Audit Your Backlinks Regularly: Use tools to scan your link profile and look for suspicious activity.
- Avoid “Link Packages”: Never buy a service that promises a specific number of links for a set price.
- Vet Every Partner: Look at the about page and contact info of every site before you agree to a link.
- Focus on Entity Building: Build a brand that exists across social media and other platforms to prove you are a real business.
- Say No to Unsolicited Emails: Most emails offering “high DR guest posts” for a small fee are selling links on link farms.

Expert Insight on Ethical Growth
Search engine algorithms have become incredibly advanced. They no longer just count links only, but they analyze the relationship between the two sites. The most effective link-building approach is to build something so good that it would be a crime for others not to link to it” is a common theme among the most reputable SEO professionals.
When you consider what link farming is and why it is ineffective, you will understand that there are no shortcuts. The secret to long-term growth is to offer a solution to a problem and let the community find that out on their own.
Conclusion
The term “link farming” is easy to define. It is a shortcut that leads to a dead-end street. While the lure of fast rankings may be very tempting, the danger of a lifetime ban is simply too great. By avoiding link farms and earning a reputation as an authority, you will protect your investment and create a brand that people and search engines trust.
The secret to effective SEO is to build your success on a foundation of quality and relevance. First, build the best content in your niche and develop real relationships with other content publishers. By doing so, you can be assured that your website will continue to grow and thrive in the constantly shifting online world.
FAQs
Can a link farm ever be useful?
No, it is almost always harmful and can lead to a total loss of search visibility.
How do I know if I am accidentally using a link farm?
Check your backlinks for sites with zero traffic and unrelated content topics.
What is the difference between a link farm and a PBN?
A link farm is a public site selling links, while a PBN is a private network of sites.
How do I get out of a link farming penalty?
You must remove or disavow the bad links and then request a review from the search engine.
Is guest posting the same as link farming?
Guest posting on a real site with a real audience is a safe and healthy tactic.
How does Google detect a link farm?
Google uses algorithms to find sites with no traffic that only exist to link out./